What is Collaborative Publishing and its challenges?
Collaborative publishing is an innovative approach to scholarly and professional publishing that emphasizes teamwork, open access, and the exchange of…

What is Scholarly Publishing and its benefits?
Introduction to Scholarly Publishing Scholarly Publishing play an important role in expanding Scholarly knowledge by enabling scientists, researchers, and professionals…

What is Academic Publishing and its impacts?
Introduction of Academic Publishing Academic Publishing journals play a vital role in disseminating knowledge and research tools in various fields.…

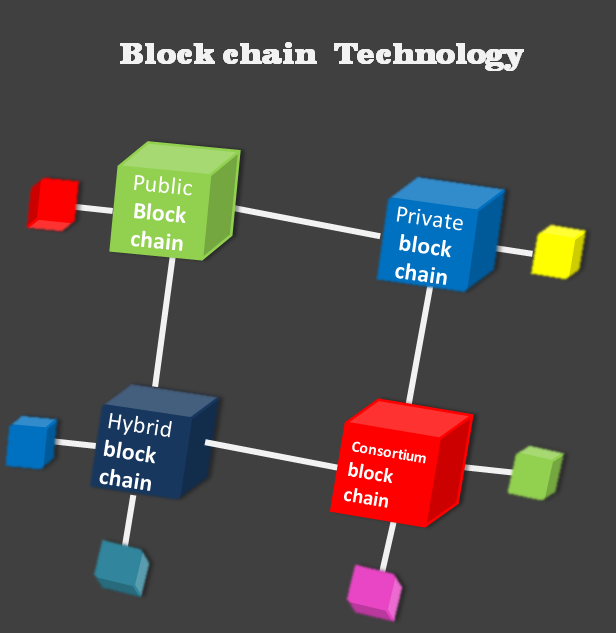
What is Blockchain technology and its challenges?
Interdiction of Blockchain technology Blockchain technology is the broad technology originally developed for currencies like Bitcoin and Crypto. These are…

What is the Back Up and recovery and its benifits?
Back Up and recovery Introduction In this modern era, data has become the needs of business people, due to which…

What is Emerging technology and its Impacts?
Emerging technology Emerging technology is revolutionizing this modern century. Thanks to which our daily thing are changing . For example,…

What is the Book Publishing and its impacts?
Introduction of Book Publishing Book publishing involves several stages, from developing the initial idea to delivering the final published book.…

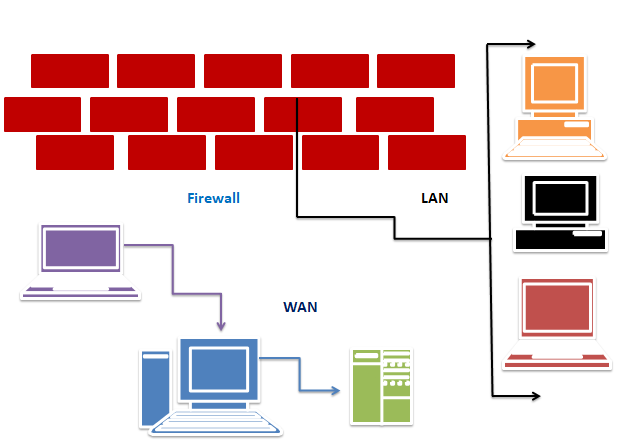
What is Network Security and Firewalls?
Introduction of Network Security and Firewalls Network security and firewalls play an important role in protecting. And ensuring networks to…

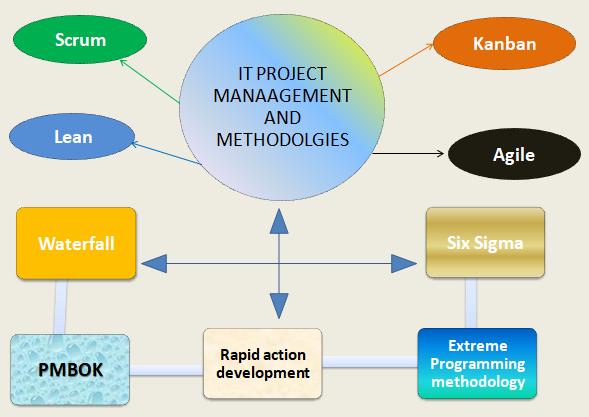
What is the IT Project Management Methodologies and its types?
Introduction of IT Project Management Methodologies IT Project Management Methodologies and working on projects in different ways. Including web development…
Author: Muhammad AllamGeer
Author: Muhammad AllamGeer
Copyright © 2025 | All Rights Reserved. Designed by 360 Web Sol.