Interdiction of Blockchain technology
Blockchain technology is the broad technology originally developed for currencies like Bitcoin and Crypto. These are applications that have powerful tools that require trust without encryption, such as fiancé supply chain and healthcare.
Define Block chain
A blockchain is a digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, making it virtually impossible to alter. This is a step which each block of data is linked to the previous block to form a secure chain. It is a technology that ensures transparency and security by eliminating the need for a central authority.
Example blockchain
A well- known example of this technology is bitcoin where transactions are recorded on a public blockchain which can be accessed by anyone, Ensuring that peer-to – peer financial transactions are carried out without a central bank.
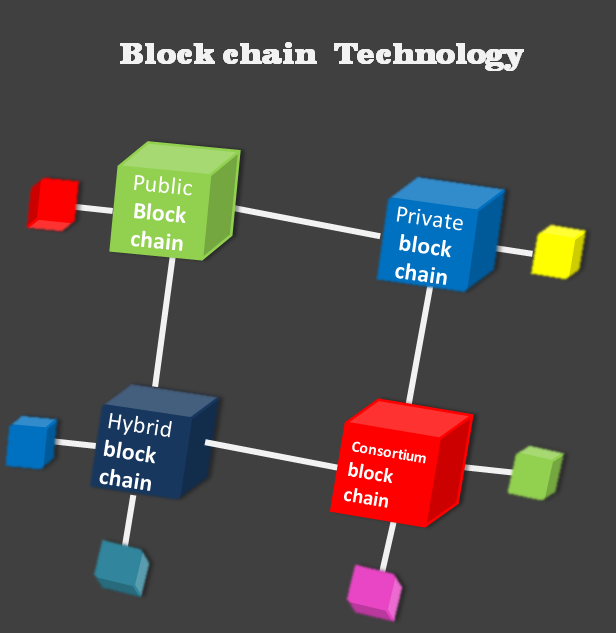
Type of blockchain
Public Block chain
Open to anyone, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, provides liquildity but requires high computing power.
Private block chain
Limited access to specific participants for enterprise use such as supply chain management.
Consortium block chain
Useful for collaborative industries like banking run by a small number of organizations
Hybrid block chain
Combines public and private elements used in application that require both transparency and privacy such as government projects.
How block chain Works
- Transaction invitation:
Transaction can be sent to the network
- Verification:
Nodes can be verify the transactions validity
- Block Creation:
Verified transactions are grouped into blockchain
- Consensus Mechanism:
Nodes are agree on the block legitimacy
- Adding to Block chain:
The block is added to the chain to finalizing the transaction
Benefits of blockchain
Block chain’s decentralization, transparency and immutability are key to making it secure and ideal for applications that require data integrity. These financial transactions are very beneficial for data storage and many more.
Applications
- Finance:
Enables secure transactions without intermediaries.
- Supply chain:
Provides transparent tracking of products from origin delivery.
- Health Care:
Stores patient records with selected access.
- Voting:
Ensures that the voting system is protected from tampering.
Challenges of Blockchain technology
Blockchain to scale inverse energy consumption Obstacles such as regulatory concerns and complexity are which may hinder mass adoption.
Future of blockchain
The future of blockchain promises innovation in areas such as cross- border payments, digital identity and data security. As technology continues to evolve, blockchain may become essential to the digital landscape.
Conclusion
Blockchain is changing industries by providing a secure and transparent way to handle data. Of course there are challenges as the potential impact of technology on finance, health care and more is undeniable, which paves the way for a secure digital future.
360 Websol





Leave a Reply